Ready to find a career and not just a job? Echelon Services is looking to expand our Team!
Working Hours:
Monday - Friday :
8:00AM to 4:30PM
Saturday & Sunday :
By Appointment Only
Professional Ceiling Fan & Ventilation System Services
Modern residential ventilation systems deliver measurable improvements in indoor air quality while reducing energy consumption by up to 48% compared to standard models[1]. Professional installation of ENERGY STAR certified ceiling fans and ventilation systems provides homeowners with enhanced comfort, moisture control, and compliance with current building codes, particularly ASHRAE 62.2 requirements that mandate specific airflow rates for residential spaces[2].
Why Proper Ventilation Matters in 2025
Contemporary residential construction emphasizes energy efficiency through improved insulation and air sealing, creating homes that are practically airtight. While this approach saves energy, it makes proper mechanical ventilation essential for maintaining acceptable indoor air quality[3]. The Environmental Protection Agency reports that people spend approximately 90 percent of their time indoors, where air can be more seriously polluted than outdoor air in even the largest industrialized cities[4].
Three primary drivers shape current ventilation requirements. First, comfort and health considerations demand effective moisture control, particularly in bathrooms where humidity levels rise significantly during use, creating breeding grounds for mold, mildew, and microorganisms that negatively impact occupant health[5]. Second, energy efficiency mandates from programs like ENERGY STAR Version 3 now require compliance with ASHRAE 62.2 ventilation standards for federally funded projects[6]. Third, code compliance has evolved beyond basic exhaust requirements to encompass whole-building ventilation strategies that balance indoor air quality with energy performance.
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers recommends a ventilation rate of 0.35 air changes per hour for new homes, with some new constructions built to even tighter specifications requiring particular attention to prevent indoor air pollutant buildup[7]. Safety constraints include proper electrical installation per National Electrical Code guidelines, adequate structural support for ceiling-mounted equipment, and appropriate ductwork sizing to prevent backdrafting or inadequate airflow performance.
Service Coverage & Options
Included Services
Echelon Services provides comprehensive ceiling fan and ventilation system services encompassing the full spectrum of residential air movement solutions. Our certified technicians handle ceiling fan installation and repair for both standard and hugger-style units, ensuring proper electrical connections and optimal performance. Attic fan services include powered ventilator installation and maintenance to achieve recommended airflow rates of 0.7 CFM per square foot of attic floor space, plus 15% additional capacity for dark roofs per Home Ventilating Institute guidelines[8].
Bathroom exhaust fan services address local ventilation requirements mandated by ASHRAE 62.2, which specifies minimum 50 CFM intermittent ventilation or 20 CFM continuous ventilation for bathroom spaces[9]. Range hood installation and service ensure kitchen ventilation meets the standard requirement of minimum 100 CFM intermittent ventilation or 5 air-changes-per-hour continuous ventilation[10]. All installations incorporate ENERGY STAR certified equipment when available to maximize energy efficiency and performance.
Typical Use Cases
New installations typically involve whole-home ventilation planning during construction or major renovation projects, where proper ductwork routing and electrical infrastructure can be integrated systematically. Replacement projects address failing or inadequate existing equipment, often upgrading from older, less efficient models to ENERGY STAR certified units that use 48% less energy than standard models[11]. Upgrade scenarios frequently involve noise reduction, where homeowners replace loud existing fans with units rated at 1.0 sones or less for quiet operation equivalent to refrigerator sound levels[12].
Ventilation balancing services address homes where airflow distribution creates comfort or moisture problems in specific areas. CFM optimization ensures each space receives appropriate ventilation based on room size and use patterns, while noise mitigation projects focus on reducing operational sound levels through proper equipment selection and installation techniques.
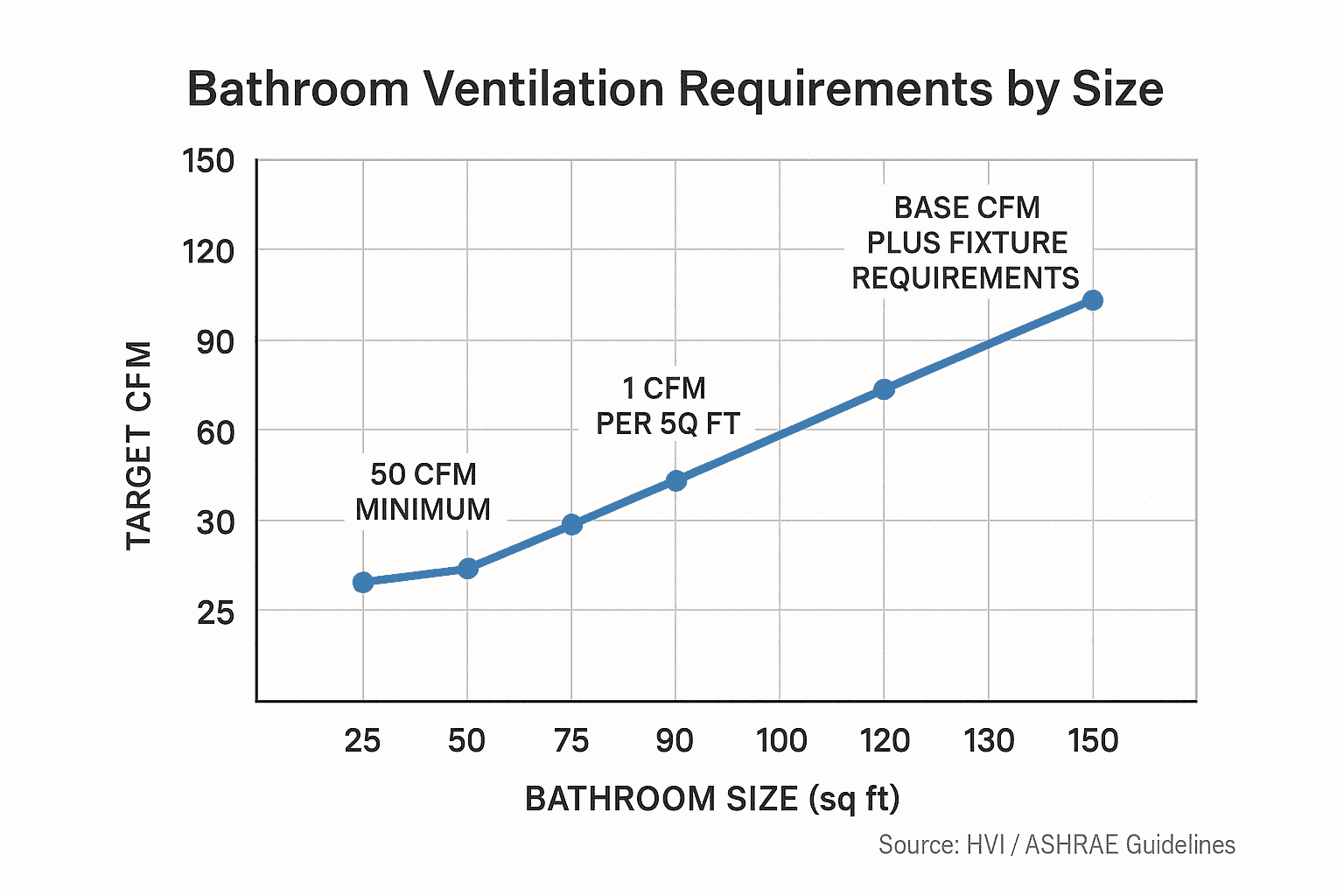
| Room Type | Size Range | Minimum CFM Required | HVI Guideline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Bathroom | ≤50 sq ft | 50 CFM | Absolute minimum regardless of size |
| Standard Bathroom | 50-100 sq ft | 1 CFM per sq ft | Based on 8 air changes per hour |
| Large Bathroom | >100 sq ft | Base CFM + fixtures | Add 50 CFM per toilet, shower, tub; 100 CFM per jetted tub |
| Kitchen | All sizes | 100 CFM intermittent | Or 5 ACH continuous |
| Attic Space | Per sq ft floor | 0.7 CFM per sq ft | +15% for dark/steep roofs |
Safety, Codes & Sizing Essentials
ENERGY STAR certified ceiling fans demonstrate up to 44% greater efficiency than conventional models through improved motor designs and optimized blade configurations[13]. Efficiency requirements vary by fan diameter, with units 36 inches and smaller requiring minimum 0.72*D + 41.93 CFM per watt performance, while larger fans between 36 and 78 inches must achieve 2.63*D – 26.83 CFM per watt efficiency[14]. These specifications ensure adequate air movement while minimizing energy consumption, particularly important given that if all residential ventilation fans sold in the United States were ENERGY STAR certified, annual energy cost savings would reach $300 million with prevention of 3.4 billion pounds of greenhouse gas emissions[15].
ASHRAE 62.2 establishes the foundation for residential ventilation sizing through its whole-building ventilation formula: 7.5 CFM per person (using bedrooms plus one for occupancy calculation) plus 1% of house square footage[16]. For example, a 3-bedroom, 1,800 square foot home requires 30 CFM for occupants plus 18 CFM for dilution ventilation, totaling 48 CFM continuous whole-building ventilation. Local exhaust requirements operate independently, mandating 50 CFM intermittent or 20 CFM continuous bathroom ventilation, plus 100 CFM intermittent or 5 ACH continuous kitchen ventilation.
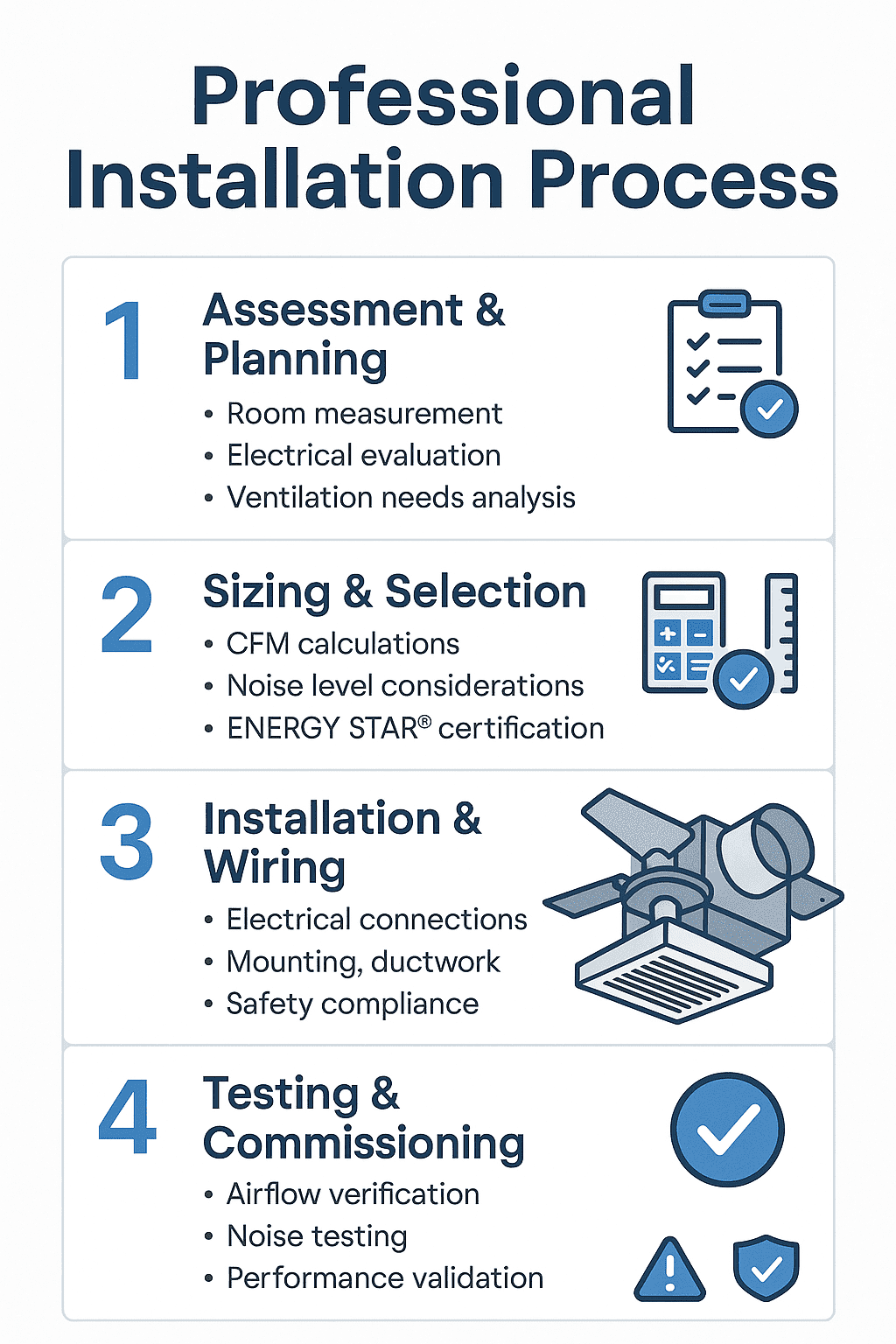
Installation Process, Quality & Limitations
Professional installation begins with comprehensive assessment and planning, including room measurement for proper equipment sizing, electrical evaluation to ensure adequate circuit capacity and appropriate wiring methods, and ventilation needs analysis based on room usage patterns and existing airflow characteristics. Sizing and selection involves CFM calculations using ASHRAE 62.2 formulas, noise level considerations to achieve target sound levels of 1.0 sones or less for quiet operation, and verification of ENERGY STAR certification for maximum efficiency benefits[17].
Installation and wiring procedures require electrical connections compliant with National Electrical Code requirements, proper mounting techniques to ensure structural integrity and minimize vibration transmission, appropriate ductwork sizing and routing to prevent airflow restrictions, and safety compliance including proper grounding and circuit protection. Testing and commissioning verify airflow performance meets design specifications, noise levels fall within acceptable ranges, and overall system performance validates design assumptions.
Quality considerations include HVI-Certified product selection, which provides assurance of independently tested and verified performance ratings. HVI certification prevents inflated performance claims common in non-certified products, ensuring ventilation expectations and building code requirements are met through rigorous laboratory testing and ongoing market verification[18]. Installation quality depends on proper ductwork design, with smooth, straight runs minimizing airflow resistance and appropriate duct sizing preventing velocity-induced noise.
Limitations and risks include undersized ductwork that restricts airflow regardless of fan capacity, creating inadequate ventilation despite proper equipment selection. Backdrafting presents particular concerns in weatherized or tightly constructed homes, where combustion appliances may not receive adequate supply air if ventilation systems create excessive negative pressure. Old wiring may lack capacity for modern equipment, requiring electrical upgrades before installation. Attic moisture conditions can affect ductwork integrity and insulation performance, while structural limitations may restrict mounting options or require additional reinforcement for ceiling-mounted equipment.
Action Plan for Homeowners
Homeowners should begin ventilation planning by measuring room dimensions to calculate square footage for CFM requirements using HVI guidelines. Bathroom spaces require minimum 50 CFM for rooms 50 square feet and smaller, or 1 CFM per square foot for larger spaces, with additional capacity needed for multiple fixtures[19]. Kitchen areas need minimum 100 CFM intermittent ventilation or 5 air-changes-per-hour continuous operation. Document existing ventilation equipment performance, noting operational noise levels and apparent airflow effectiveness during high-moisture activities.
Noise goals should target 1.0 sones or less for quiet operation, equivalent to refrigerator sound levels that won’t interfere with normal household activities[20]. Sound levels above 3.0 sones (typical office noise) may create user resistance, leading to reduced usage and inadequate ventilation performance. Consider bathroom door clearance requirements of at least three-quarters inch to floor level, ensuring adequate makeup air entry for proper exhaust fan operation.
Ductwork path evaluation identifies potential installation challenges and performance limitations. Existing ductwork should be inspected for proper sizing, smooth interior surfaces, and direct routing to exterior terminations. Flexible ductwork creates higher airflow resistance than rigid ducting, potentially reducing fan performance below rated specifications. Attic access, exterior wall penetration options, and structural considerations affect installation complexity and final system performance.
Schedule professional evaluation with qualified electrical contractors experienced in residential ventilation systems. Licensed electricians can assess electrical capacity, recommend appropriate equipment based on specific room requirements, and ensure installations meet current National Electrical Code requirements. Professional assessment prevents common sizing errors and identifies potential complications before project initiation, ensuring realistic expectations and proper system performance.
For immediate assistance with ceiling fan and ventilation system planning, contact Echelon Services at our contact page to schedule a comprehensive evaluation. Our certified technicians provide detailed assessments, equipment recommendations, and professional installation services throughout our service area.
Future Outlook
Smart ventilation controls represent the next evolution in residential air quality management, integrating humidity sensors, occupancy detection, and automated scheduling to optimize ventilation timing and duration. Advanced systems monitor indoor air quality parameters including volatile organic compounds, particulate matter, and carbon dioxide levels, adjusting ventilation rates dynamically based on actual conditions rather than fixed schedules. These technologies promise improved energy efficiency through demand-controlled ventilation while maintaining superior indoor air quality.
Electronically commutated motor (ECM) technology delivers significant efficiency improvements over traditional permanent split capacitor motors, with some applications achieving 70% energy reduction compared to standard models[21]. ECM motors maintain consistent airflow across varying static pressure conditions, providing more predictable performance in real-world installations where ductwork creates airflow resistance. Variable speed operation enables precise airflow control and reduced noise levels during low-demand periods.
Humidity and indoor air quality integration expands ventilation system capabilities beyond simple exhaust functions. Heat recovery ventilators and energy recovery ventilators capture thermal energy from exhaust air streams, reducing heating and cooling loads while providing continuous fresh air supply. These systems address whole-building ventilation requirements more efficiently than traditional exhaust-only approaches, particularly in climate zones with significant heating or cooling demands.
However, implementation risks include poor ductwork design that negates advanced equipment benefits, creating system performance below design expectations regardless of technology sophistication. Building code updates may require retroactive compliance for existing installations, potentially mandating system upgrades or modifications. Integration complexity with existing HVAC systems can create compatibility issues, requiring specialized expertise for proper installation and commissioning. Homeowners should consider these factors when planning ventilation system investments, balancing advanced features against installation complexity and long-term maintenance requirements.
Key Takeaways
- Target minimum 1 CFM per square foot for bathrooms 50-100 square feet, with 50 CFM absolute minimum for smaller spaces per ASHRAE 62.2 and HVI guidelines[22]
- ENERGY STAR certified ventilation fans use 48% less energy than standard models, with potential national savings of $300 million annually if universally adopted[23]
- Noise levels should not exceed 1.0 sones for acceptable residential operation, equivalent to quiet refrigerator sound levels[24]
- Whole-building ventilation requires 7.5 CFM per occupant plus 1% of floor area, independent of local exhaust requirements[25]
References
- ENERGY STAR Ventilation Fans | US EPA
- ASHRAE 62.2 for New Construction – HVAC Design Pros
- The Inside Story: A Guide to Indoor Air Quality | US EPA
- The Inside Story: A Guide to Indoor Air Quality | US EPA
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans – Home Ventilating Institute
- ASHRAE 62.2 for New Construction – HVAC Design Pros
- The Inside Story: A Guide to Indoor Air Quality | US EPA
- HOME VENTILATING FANS – HVI Publication
- ASHRAE 62.2 for New Construction – HVAC Design Pros
- ASHRAE 62.2 for New Construction – HVAC Design Pros
- ENERGY STAR Ventilation Fans | US EPA
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans – Home Ventilating Institute
- Ceiling Fans | ENERGY STAR
- Ceiling Fans Key Product Criteria | ENERGY STAR
- ENERGY STAR Ventilation Fans | US EPA
- ASHRAE 62.2 for New Construction – HVAC Design Pros
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans – Home Ventilating Institute
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans – Home Ventilating Institute
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans – Home Ventilating Institute
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans – Home Ventilating Institute
- ENERGY STAR Ventilation Fans | US EPA
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans – Home Ventilating Institute
- ENERGY STAR Ventilation Fans | US EPA
- Bathroom Exhaust Fans – Home Ventilating Institute
- ASHRAE 62.2 for New Construction – HVAC Design Pros

